Audit and Acceptance Sampling Solutions
Science-Based Tools for Utility-Oriented Quality Assessment
From Error Rates to Utility
Traditional standards such as ISO 2859 or ISO 3951 focus on producer’s and consumer’s error rates, often leading to unnecessarily large sample sizes.
QuoData embraces the utility-based approach which goes further: instead of looking only at the probability of errors, the utility-based approach considers the full cost–benefit profile of a decision. Economic gains, inspection and recall costs, potential health impacts, and reputational damage are all built into a mathematically defined utility function. This enables rational, calculated risk-taking rather than stifling innovation through excessive risk aversion—yielding smaller sample sizes, better protection profiles, and transparent, traceable decisions.

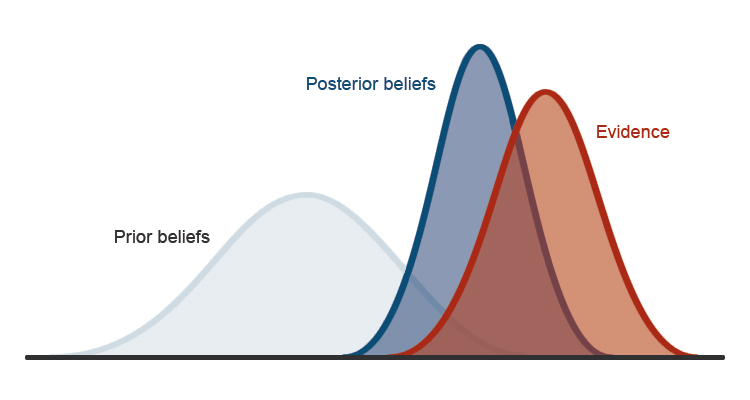
Bayesian Statistics – Forward-thinking Decision-Making
QuoData applies methods grounded in Bayesian statistics, which integrate prior knowledge with new data to produce decisions that reflect both historical evidence and current measurements.
This allows our team to optimize sampling plans even when data are scarce, to quantify uncertainty realistically, and to adapt inspection strategies as more information becomes available. Hierarchical Bayesian models and regret functions help ensure that plans remain robust, evidence-based, and defensible.
Applications Across Industries
QuoData solutions are applicable wherever reliable acceptance decisions are crucial, including:
- Food safety and agricultural inspections
- Pharmaceutical and medical device quality control
- Materials science and manufacturing process monitoring
- AI system evaluation and conformity-classification sampling
- Litigation and forensic investigations, where statistically defensible quality evidence can be decisive
Adaptable Solutions
QuoData provides its solutions to you in three flexible formats:
- Individual expert service – bespoke consulting for unique problems.
- Pilot projects – proof-of-concept studies to evaluate feasibility and value.
- Standardized tools – ready-to-use software and procedures for routine application.

Collaborate with a Leader in International Standards and Research
QuoData plays a leading role in advancing statistical quality assurance on the ISO level, contributing to the development of standards and continually publishing in collaboration with national metrology institutes (NMIs), regulatory bodies, and other key stakeholders. QuoData is committed to refining and disseminating approaches that combine scientific rigor with practical applicability.
Let’s turn your quality challenges into measurable success
Get in touch for a consultation and explore how our utility-based acceptance sampling solutions can transform your inspection strategy.
Advanced Statistical Quality Control – Core Principles in Brief
- Acceptance Sampling: A statistical quality control method in which a decision to accept or reject a lot is based on inspecting a sample rather than every item. It balances inspection costs with the risk of accepting defective items.
- Producer’s error rate: represents the probability of rejecting a good lot that actually meets quality standards
- Consumer’s error rate: represents the probability of accepting a batch that is defective, i.e., the chance of incorrectly accepting a lot with a high defect rate
- Utility Function in Quality Control: A mathematical expression combining benefits, costs, and potential damages into a single value. Maximizing utility leads to inspection strategies that are both cost-effective and protective of quality.
- Bayesian Statistics: A statistical framework that updates the probability of an event as more information becomes available, combining prior knowledge with new data for better decision-making under uncertainty.
- Regret Function: A tool for evaluating the difference between the chosen plan’s cost and the lowest possible cost, helping to fine-tune sampling strategies.
Learn more: QuoData papers
The QuoData team contributed to several papers in the field, e.g.:
- Acceptance Sampling Plans Based on Utility Functions—Inspection of Lots and Processes by Attributes Uhlig, S.; Colson, B.; Göb, R.; Pennecchi, F.; Ellis, S.; Hicks, M.; Vandenbemden, J.; Kissling, R.; Gowik, P. - Preprints 2025, 2025041544.
- Acceptance Sampling Plans Based on Conformance Probability—Inspection of Lots and Processes by Attributes Uhlig, S.; Colson, B.; Kissling, R.; Ellis, S.; Hicks, M.; Vandenbemden, J.; Pennecchi, F.; Göb, R.; Gowik, P. - Preprints 2024, 2024092228.
- Application of the Bayesian Conformity Assessment Framework from JCGM 106:2012 for Lot Inspection on the Basis of Single Items Uhlig, S.; Colson, B.; Göb, R.; Gowik, P. - Preprints 2022, 2022060032.
- A Procedure for Estimating Fundamental Variability Uhlig, S.; Colson, B.; Gowik, P. - Preprints 2022, 2022110460.
